From early morning practices to Friday night lights, high school sports play a major role in student life. With the intensity and physical demands of competition, though, comes the real risk of injuries. Some are mild and resolve quickly, but others can interrupt a season or lead to long-term setbacks. The good news? Many of the most common sports injuries in teens are entirely preventable with the right approach to training, recovery and care.
Understanding the most common high school sports injuries can help athletes, coaches, and parents reduce risk and stay focused on the game. Here are five of the most frequent injuries seen in young athletes, how they happen, how they're treated, and what can be done to keep them from happening in the first place.
1. Ankle Sprains: The #1 High School Sports Injury

Ankle sprains top the list for high school athletes, especially in sports like basketball, soccer and track. These injuries occur when the ligaments that support the ankle joint are overstretched or torn, often after the foot rolls, twists or lands in an unstable position. Sprains can range from mild to severe, but even a mild one can limit movement and cause swelling and pain. Treatment typically includes early rehabilitation and movement, rest, ice, compression and elevation (R.I.C.E.), and in more serious cases or temporary bracing.
The good news is that ankle sprains are often preventable. Strengthening exercises, balance drills and wearing properly fitted, sport-specific footwear can go a long way. An ankle brace may also be helpful for athletes with a history of sprains.
"A properly supported and strengthened ankle is the first line of defense against injury in high-impact sports," says Courtney Conklin, M.D., a fellowship trained, board-certified sports medicine physician with Riverside Orthopedic and Sports Medicine Specialists.” Many of the sprains we treat likely could have been avoided with ankle mobility exercises and supportive footwear or an ankle brace."
2. Knee Injuries: From Overuse to ACL Tears
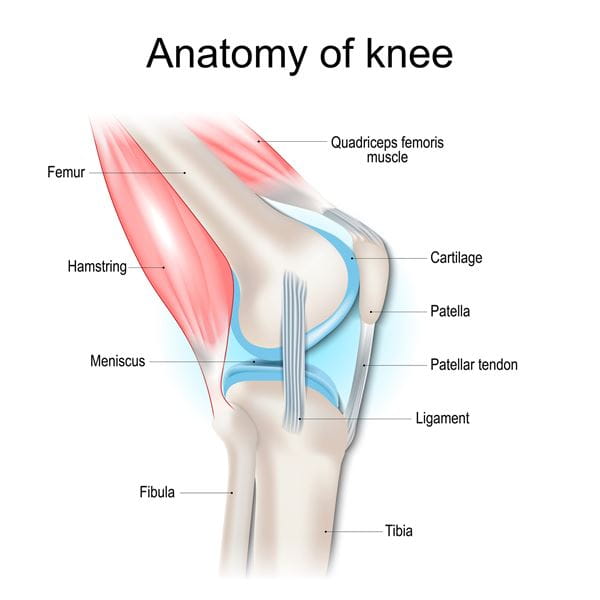
Knee injuries are another common challenge. These include ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) tears, meniscus damage, and overuse injuries like patellar tendinitis. They're most often seen in sports that involve pivoting, jumping and sudden stops – like soccer, basketball, volleyball and football.
ACL and meniscus injuries can require surgical repair, while tendinitis often calls for rest, stretching and physical therapy. The root cause is often a combination of poor landing technique, weak core and leg muscles, or simply overtraining.
Preventing knee injuries involves strengthening the muscles that support the joint, learning proper mechanics for cutting and jumping, and mixing up training routines to avoid overuse. Limiting specialization in a single sport can also reduce repetitive strain.
3. Shoulder Injuries: A Risk for Overhead Athletes
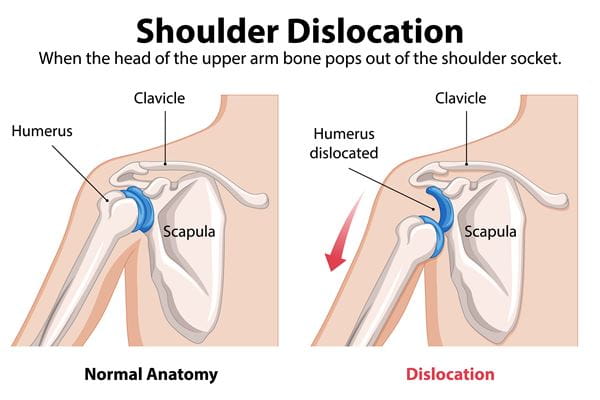
Shoulder injuries are common in overhead sports like baseball, swimming, softball and volleyball. These often involve strains to the rotator cuff, joint instability or even dislocations. Repetitive motion and fatigue are major contributors, especially when proper form breaks down.
Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, or, in some cases, surgery, particularly for repeated dislocations. Prevention hinges on maintaining shoulder strength and flexibility, following pitch count recommendations and not ignoring early signs of soreness.
Athletes and coaches should emphasize proper technique, especially in young athletes who are still developing muscle coordination and strength.
4. Concussions: More Than a Bump on the Head

Concussions are commonly referred to as “mild traumatic brain injuries” since they don’t typically pose an immediate threat to life, but that doesn’t mean they shouldn’t be taken seriously. Concussions are caused by a blow to the head or body that shakes the brain, and they are particularly common in football, soccer, lacrosse and cheerleading, or any sport where collisions or falls are part of the game.
Common symptoms of a concussion may include headache, confusion, dizziness, nausea, sensitivity to light or noise, and changes in mood or sleep. Immediate removal from play is essential, followed by a gradual return to activity under medical supervision.
"Concussions aren't always obvious,” notes Dr. Conklin, “dizziness, confusion, or even mood changes after a hit should be taken seriously and you should seek care from a medical provider for immediate evaluation.”
To prevent concussions, athletes should wear well-fitted helmets, follow safety rules and learn to recognize early symptoms. Teaching safe play and encouraging players to speak up when something feels off is crucial.
5. Growth Plate Injuries: Repeated Stress Can Cause Long-term Injury
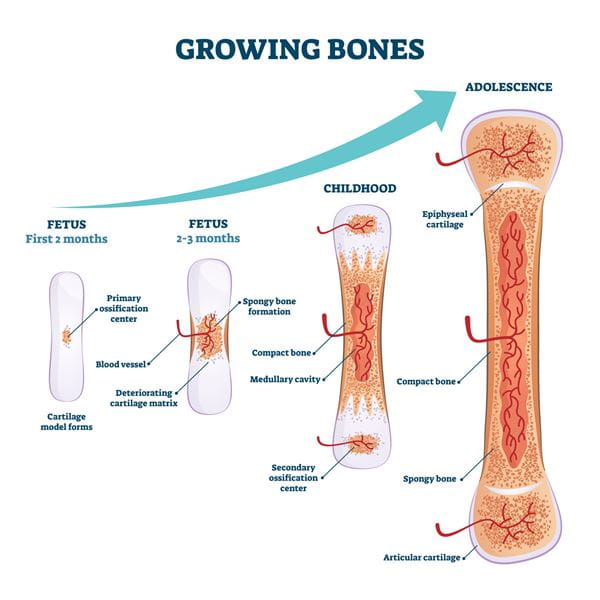
Growth plates are areas of developing tissue at the ends of long bones. In teens, these plates are vulnerable to injury, especially from repetitive stress. Sports like gymnastics, baseball and track can put young athletes at risk due to their repetitive movements such as jumping, throwing, and running.
These injuries can affect future bone growth if not treated properly. Common signs include pain near joints, swelling or difficulty with movement. Treatment may involve rest, immobilization or physical therapy, and rarely, surgery.
Preventing growth plate injuries means encouraging rest periods during the year, avoiding early specialization and watching for signs of overuse. Parents and coaches should stay alert to any pain that persists or worsens during growth spurts.
Final Thoughts: Smart Habits Make Safer Athletes
While injuries are a part of sports, many can be prevented with smart training and awareness. High school athletes should be encouraged to warm up properly, cross-train, avoid overtraining and listen to their bodies. Proper nutrition, hydration and sleep also play an important role in injury prevention.
And if an injury does happen, early treatment matters. Getting care quickly can prevent long-term damage and help athletes return to their sport safely and confidently. Reach out to a Riverside Sports Medicine Specialist by calling the Sports Medicine Hotline at 757-534-6767 or schedule an appointment online.
With the right support and preparation, student-athletes can stay strong all season and enjoy all the benefits that sports have to offer.